

Tinea capitis is also called ringworm of the scalp, but it’s not caused by a worm. It’s a fungus infection. A fungus is a germ that is too small to see.
Ringworm is very contagious (spreads easily) among children. It most often happens in children 4 to 7 years old. However, it can happen in children as young as 1 year of age. It is rare in adults.
How the Infection Spreads
The fungus usually spreads when a child:
- Comes in direct contact with the head or hairs of someone who has ringworm.
- Uses a comb, brush, hat, stuffed toy, towel, or pillowcase of an infected person.
- Comes in contact with an infected animal.
Symptoms
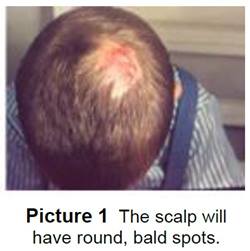
- Ringworm can be on parts of the scalp or all of it. The scalp will have:
- Round, bald patches with black dots where the hair has broken off (Picture 1). Blonde-haired children will have blonde dots.
- Dry raised scales and crusty bumps. These might drain pus and be tender.
- Itchiness.
- Sometimes a child may have lumps (swollen glands) in the neck and back of the head.
- Ringworm usually doesn’t cause fevers.
Diagnosis
Your child’s doctor or health care provider can tell if they have ringworm by the way their scalp looks. Sometimes, they may send a bit of the scaly skin and/or hairs for testing. It usually takes 2 to 3 weeks to get the test results back.
Treatment
Ringworm won’t go away on its own. Medicine and a special antifungal shampoo can cure it. Treatment should start early to prevent scarring or damage to the scalp. It may take many weeks to go away.
- Your child’s doctor or health care provider will prescribe a medicine to be taken by mouth for 1 to 3 months. The medicine goes through the blood to the scalp and into the growing hairs to stop the fungus from growing.
- With some medicines, your child may need to eat fatty foods, such as whole milk, cheese, ice cream, or yogurt to help the medicine work better
.
- The infection may come back if your child stops the medicine too early
Prevention
- No one should share combs, hairbrushes, hats, stuffed toys, towels, or pillowcases with others.
- Soak combs and hairbrushes in a mixture of half bleach and half water for 1 hour each day. Do this for the first 3 days after you start giving the medicine and using the antifungal shampoo.
- Wash towels in warm, soapy water after each use. Rinse and dry.
- Wash your hands after touching pets and animals.
- Some OTC dandruff shampoos (Selsun Blue® or Head and Shoulders®) can help prevent the spread of the fungus. Ask your doctor or health care provider about these.
More Information
- Some children who have ringworm need to stay home from school. Your child’s doctor or health care provider will tell you when they may go back.
- If your child takes the medicine for longer than 6 to 8 weeks or needs to repeat the course of treatment, they may need blood tests to check for side effects of the medicine.
- The places where hair has fallen out will usually grow back after your child finishes their treatment. It may take several months.
When to Call the Doctor
- Call your child’s doctor or health care provider if:
- The infection is not getting better after 4 weeks of therapy.
- Patches on their scalp drain pus and are painful.
- They have a fever or temperature:
- Of 104° Fahrenheit (F) or 40° Celsius (C) or above.
- Above 102°F (38.9°C) for more than 2 days or it keeps coming back.
These things could mean that your child may also have a bacterial infection.
How to deal with scalp fungus?
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang – Dermatologist, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine – Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. The doctor has over 12 years of experience in the field of dermatology.
Scalp fungus not only causes itching, flaking, hair loss, severely affecting aesthetics but also affecting the quality of life of patients. The disease is easily confused because lesions on the scalp have many types such as impetigo, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis… and there are many types of pathogenic fungi. In fact, many cases of scalp fungus, including children, are treated by their parents according to folklore, so the scalp is severely inflamed, hair loss, and permanent scarring.
1. Scalp fungus
1.1 Tinea capitis caused by Trichophyton Scalp fungal disease begins with small, scattered nodules on the scalp. The base of the lesion has thin scaly patches, healthy hair interspersed with truncated hair near the base (due to fungal infections becoming hard and brittle).
Scales peel off the scalp forming a temporary bald patch. This disease causes itching, the patient can have fungal skin infections in other locations (inguinal, buttock, nail).
1.2 Trachoma (hair eggs) caused by the fungus Pierdraiahortai and Trichosporon beigeli Characterized by along the hair shaft, from 2-3 cm from the base of the hair, there are soft round seeds (almost the size of millet), black or brown and can shed like lice eggs. This disease does not cause hair loss because the mycelium grows only in the hair shaft, which may cause mild discomfort or itching. Diseases often arise from poor personal hygiene.
The source of scalp fungal disease is mainly humans, in addition, it can be from some animals such as dogs and cats. Fungi can persist on contaminated materials. The disease is spread directly from the skin, through the skin, but the most common way is indirectly through sharing combs, hats, pillows… with sick people.
To make a diagnosis, in addition to relying on clinical symptoms, it is necessary to do tests: Fresh examination of the specimen is a scalp scaly patch or a substance on the hair. Culture in agar medium to diagnose the fungus and have an appropriate treatment regimen.

2. Effective treatment of scalp fungus
For mild cases, daily shampooing to remove hair loss, using selenium Sulfide shampoo or Nizoral shampoo works well.
If it gets worse, after washing, you should cover your hair with a towel (pay attention when you wash your hair, don’t scratch or scratch it, causing local skin abrasions, creating conditions for bacterial superinfection)
Or you can cut all your hair. If the scalp is affected by fungus, apply a topical fungicide daily. If the lesion is infected with bacteria, apply topical antiseptic, systemic antibiotics can be used in combination.
Drug treatment options:
When topical treatments with antifungal creams and shampoos don’t work, your doctor will prescribe oral antifungal medications. The antifungal medication Griseofulvin is taken by mouth for 6–8 weeks. Patients should take Griseofulvin with a high-fat meal to enhance absorption. Griseofulvin may cause nausea or stomach upset in children. Terbinafine, Itraconazole and Fluconazole are commonly used fungicides. However, the duration of treatment for some of these drugs may be shorter, 2 to 4 weeks. Both Ketoconazole and Fluconazole can cause colic in the baby, so they should be used with caution. For scalp inflammation caused by Microsporum spp., Griseofulvin has been shown to be superior for treatment, while Terbinafine is better for Trichophyton spp. infection.
3. Remedies to reduce scalp fungus

To limit the spread of the disease, when the weather is hot, it is necessary to keep clean, especially places such as kindergartens, schools, dormitories… Use clean shampoo every day, do not scratch or scratch. strongly scratch the scalp, must rinse with clean water many times when washing hair and always keep the hair dry and clean. At the same time, make your hair dry right after you wash your hair and when you come back from the rain. Do not wear hats that are too tight, wear hats for too long to make your hair wet, easy to create favorable conditions for fungi to grow and cause disease. Avoid contact with infected pets, possibly take the pets to the vet periodically and check for fungus. Avoid sharing items with others to avoid the risk of spreading disease from people around. Do not share towels, hair combs, hats of other people, especially people with dandruff or symptoms of scalp fungal disease. Head fungus is contagious, so as soon as you feel signs of the disease, it is necessary to quickly seek medical attention and timely treatment. If detected and treated early, with the right method, with a reasonable shampoo regimen, scalp fungal disease can be cured. If there is too much dandruff on the head with signs such as itching, oily and smelly hair, red acne appears … you should see a dermatologist immediately to help find the cause and appropriate treatment. Absolutely do not scratch and scratch the scalp vigorously to avoid causing damage and causing dandruff and fungus to spread more widely. Do not arbitrarily buy drugs to drink and apply without a doctor’s prescription or advice. Eating a nutritious diet and always improving the body’s resistance is also one of the ways to prevent disease.



Leave a Reply